HOT ROLLED STEEL
(HRS)
Hot rolling is a mill process which involves rolling the steel at a high temperature (typically at a temperature over 930° C), which is above the steel’s recrystallization temperature.
Hot rolling is a mill process which involves rolling the steel at a high temperature (typically at a temperature over 930° C), which is above the steel’s recrystallization temperature.
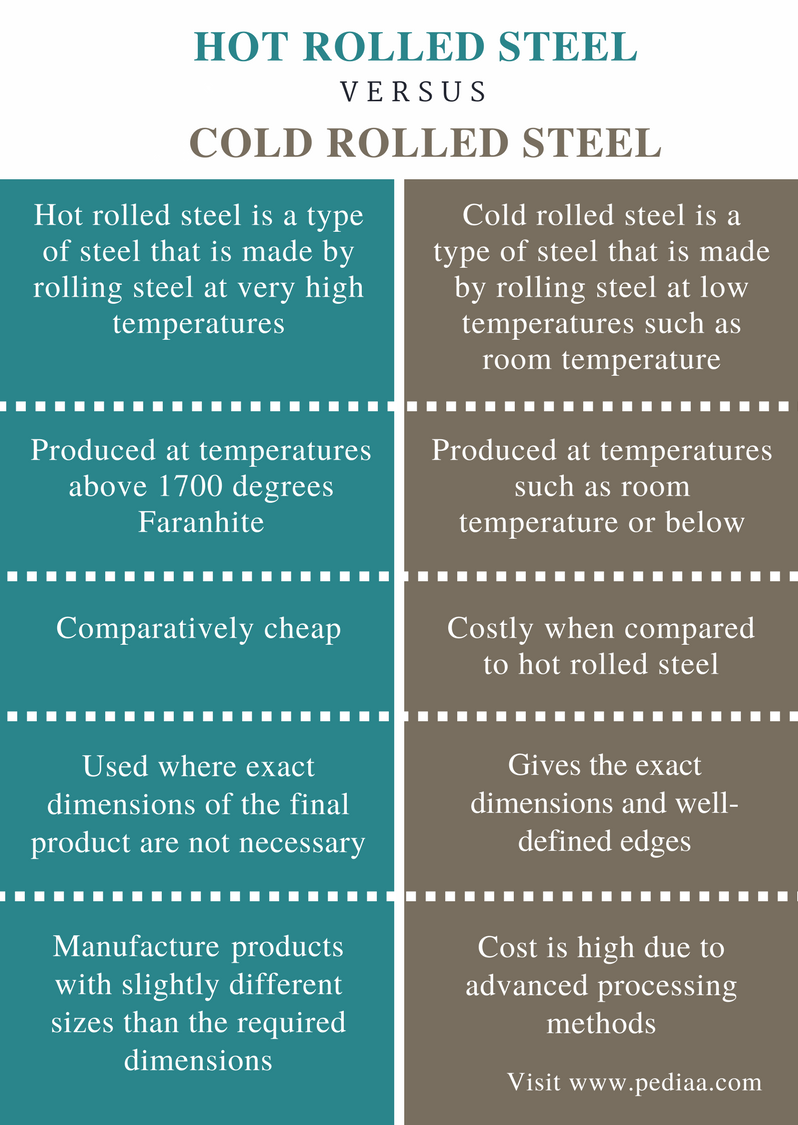
When steel is above the recrystallization temperature, it can be shaped and formed easily, and the steel can be made in much larger sizes. Hot rolled steel is typically cheaper than cold rolled steel due to the fact that it is often manufactured without any delays in the process, and therefore the reheating of the steel is not required (as it is with cold rolled). When the steel cools off it will shrink slightly thus giving less control on the size and shape of the finished product when compared to cold rolled.
- The cooling from extreme temperatures leads to a scaled surface
- Due to shrinkage hot rolled steels have slightly rounded edges and shapes
- The workpieces show slight distortions
What are the benefits of hot rolled steel?
Such types of steel are cheaper due to the fact that they do not require a lot of processing. Further, hot rolled steel is normalized because it is not quenched and cools at room temperature. This makes it free of internal stress.
As the dimensions of hot rolled steel parts are not very precise, they are used in applications where material strength and not precision or surface quality is of high importance. To improve the surface quality, the workpieces can undergo a pickling procedure. Furthermore, the scaling can be removed by grinding or sand blasting.




Our index:
Sustainability index:
price index:
#metal #HRS